Stem Cell Therapy for
Joint Pain in Chicago: Regenerative Medicine Approaches to Chronic Joint Pain
Relief
Living with chronic joint pain can wear people down. Simple movements become harder. Daily routines take more effort. Many people want relief without surgery or long recovery periods. Because of that, regenerative medicine has gained attention as a non-surgical option for joint pain.
Stem cell therapy is one approach that uses the body’s own biological processes to support joint function and reduce discomfort. For many patients in Chicago, this type of care offers another path to managing long-term joint pain. Here's why it works.
The Daily Reality of Chronic Joint Pain
Chronic joint pain goes beyond soreness after activity. It lasts for months or even years. Pain often remains despite rest, medication, or basic therapy. Over time, it can affect how people walk, work, and sleep. Activities like climbing stairs or standing for long periods may become difficult.
Joint pain often develops when parts of the musculoskeletal system begin to change. Cartilage may thin. Inflammation may increase. Old injuries can also play a role. Autoimmune conditions can worsen joint symptoms as well. Research suggests that chronic pain affects roughly 25% of Americans, showing how widespread this problem is. (1)
Why More Chicago Patients Are Exploring Regenerative Medicine
Many patients want relief without the risks that come with surgery. Surgical procedures usually require anesthesia, an extended recovery for an average of six to 12 weeks, and time away from work or family life. Even then, results aren't guaranteed. (2)
Because of this, non-surgical treatments have drawn more interest. Regenerative medicine focuses on supporting the body rather than replacing damaged joints. For people dealing with knee, hip, shoulder, or back pain that hasn’t improved with standard care, learning more about stem cell therapy for joint pain in Chicago can help clarify whether biologic treatments may be an appropriate next step.
These approaches aim to manage symptoms while allowing many patients to maintain daily routines. This shift has been especially noticeable among those who have already tried medication, injections, or therapy without lasting relief.
How Stem Cell Therapy Is Used for Joint Pain
Stem cell therapy for joint pain focuses on reducing inflammation and supporting tissue response inside the joint. Instead of removing tissue or inserting hardware, treatment works within the existing joint environment.
The Role of Adult Stem Cells in Joint Support
Adult stem cells, including mesenchymal stem cells, can release growth factors that influence how nearby tissues behave. These signals may help calm inflammation and support healthier joint movement.
Some clinical research shows that stem cell-based treatments can lead to greater pain reduction in joint conditions when compared with other biologic options. Results vary, but the data have driven continued interest in this approach.
Where Stem Cells Come From
Stem cells used in joint therapy usually come from the patient’s own body. Two common sources are used:
- Bone marrow collected from the pelvic bone
- Adipose tissue obtained through a small fat-collection procedure
These cells are considered adult stem cells. Embryonic stem cells aren't used in orthopedic joint care. Using a patient’s own cells also helps lower the risk of rejection or complications.
Joint Conditions Commonly Treated With Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy is often considered for joint problems that don't improve with rest or routine care. It's commonly explored for several conditions:
- Knee pain caused by cartilage wear or osteoarthritis
- Shoulder problems, such as rotator cuff tears or labrum tears
- Overuse injuries like tennis elbow and ligament sprains
- Ongoing hip and back pain linked to joint degeneration
Knee osteoarthritis alone has a prevalence of 365 million worldwide. That number highlights how common joint degeneration has become and why many people seek new treatment options. (3)
How Stem Cell Therapy Compares to Other Regenerative Options
Stem cell therapy isn't the only regenerative treatment available. It's often compared with other biologic approaches.
Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatments
Platelet-rich plasma therapy uses platelets drawn from a patient’s blood. These platelets release growth factors that may support tissue response. PRP is sometimes used on its own for mild joint issues. In other cases, it may be combined with stem cell therapy based on the condition being treated.
The Role of Physical Therapy
Physical therapy remains integral in joint care. Strong muscles help protect joints. Better movement patterns can reduce strain. Many treatment plans include therapy either before or after injections. When paired with regenerative care, physical therapy may help patients maintain progress over time.
What the Treatment Process Looks Like
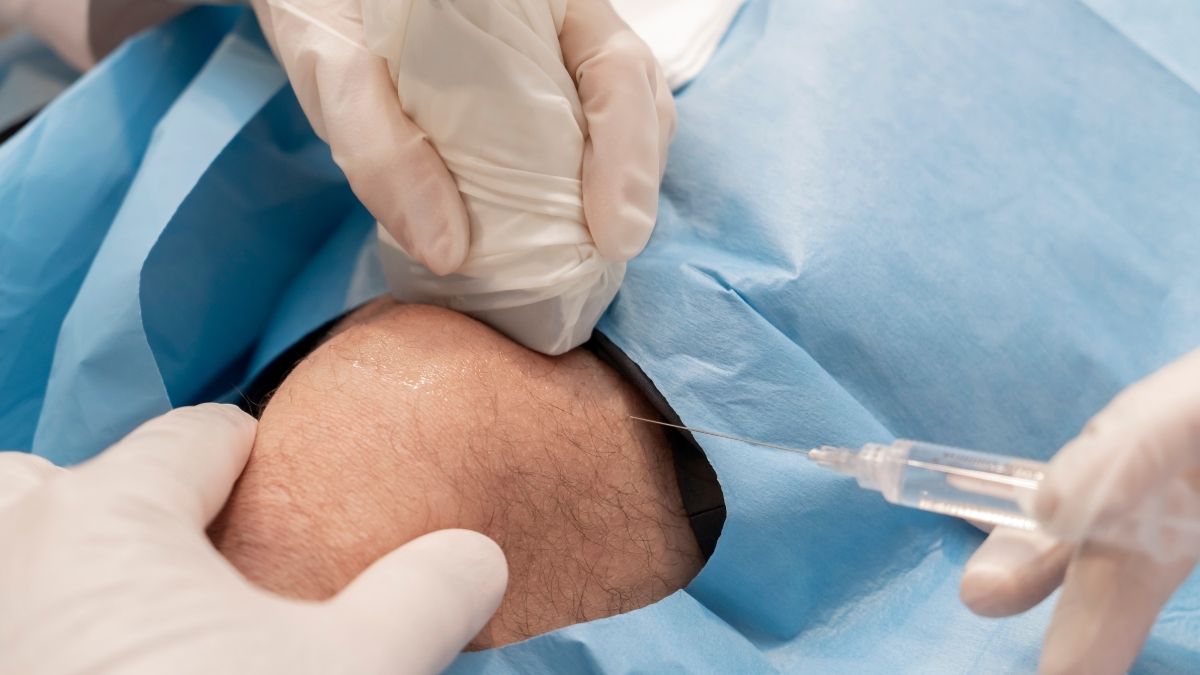
Treatment usually begins with a detailed evaluation. Imaging helps confirm the source of pain and guides injection placement. Stem cells are collected, processed, and then injected into the affected joint using imaging support.
After treatment, patients often resume light activity within a short period. Improvement may occur gradually over weeks or months. Follow-up care focuses on safe movement and realistic expectations. Not every patient responds the same way, so individual assessment remains important.
Benefits of Non-Surgical Joint Pain Relief
Non-surgical care offers several advantages for people with chronic joint pain:
- Reduced need for invasive surgical procedures
- Shorter recovery times compared with surgery
- A focus on improving comfort and movement rather than joint replacement
These benefits appeal to patients who want pain relief while staying active and independent.
Regenerative Medicine Care in Chicago and Nearby Suburbs
Across Chicago and nearby suburbs, more patients are discussing regenerative medicine with their providers. Many turn to these options after trying medication, injections, or physical therapy with limited success. Image-guided techniques and careful patient selection play a key role in treatment planning. Access to trained clinicians also helps ensure safety and precision.
Final Thoughts
Chronic joint pain can affect nearly every part of daily life. Regenerative medicine offers a non-surgical option that focuses on supporting joint health rather than replacing it. Stem cell therapy uses adult stem cells and growth factors to help manage inflammation and improve movement. For those looking to avoid surgery, these treatments offer another option to discuss when planning long-term joint care.
References
1. "Chronic Pain", Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553030/
2. "How Long Should You Wait Between Surgeries?", Source: https://www.verywellhealth.com/best-waiting-time-between-surgeries-3156968
3. "Osteoarthritis", Source: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/osteoarthritis